Tel: +86-13587713206 / +86-577-61389776丨E-mail: nancy4046@hotmail.com
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-12 Origin: Site









Selecting the right shrink tubing is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. With the wide variety of available options, including Heat Shrink Dual Wall Tubings and Stress Control Tubings, making an informed choice can prevent failures and enhance system performance.
In this article, we will discuss the key parameters for Shrink Tubing Selection, including material types, shrink ratios, wall thickness, and environmental factors. You'll gain insights into how these elements affect installation efficiency and the overall protection of electrical components.
Heat shrink tubing is made from various materials, each offering specific advantages. Polyolefin is the most common material due to its flexibility, durability, and excellent electrical insulation properties. It’s widely used for general-purpose applications. PVC, while less heat-resistant than polyolefin, is cost-effective and suitable for lower-temperature applications. PTFE (Teflon®), known for its high chemical resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures, is often used in specialized applications such as aerospace or military environments.
In environments where exposure to harsh chemicals is likely, PTFE or FEP materials are ideal. For less aggressive environments, polyolefin and PVC provide adequate chemical resistance.
Polyolefin offers excellent flexibility, making it ideal for areas that experience bending or movement. In contrast, PTFE is more rigid but offers superior resistance to extreme conditions. The choice of material should be based on both flexibility and the environmental demands of the application.
Type | Material | Key Features | Best Use Case |
Single-Wall Tubing | Polyolefin, PVC | Basic insulation and abrasion protection | Indoor applications, basic insulation |
Dual-Wall Tubing | Polyolefin + Adhesive | Waterproof, moisture-resistant | Outdoor applications, industrial environments |
Stress Control Tubing | Polyolefin, PTFE | Prevents mechanical stress at joints | High-vibration or strain-sensitive environments |
High-Temperature Tubing | PTFE, Silicone | Withstands extreme temperatures | Automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications |
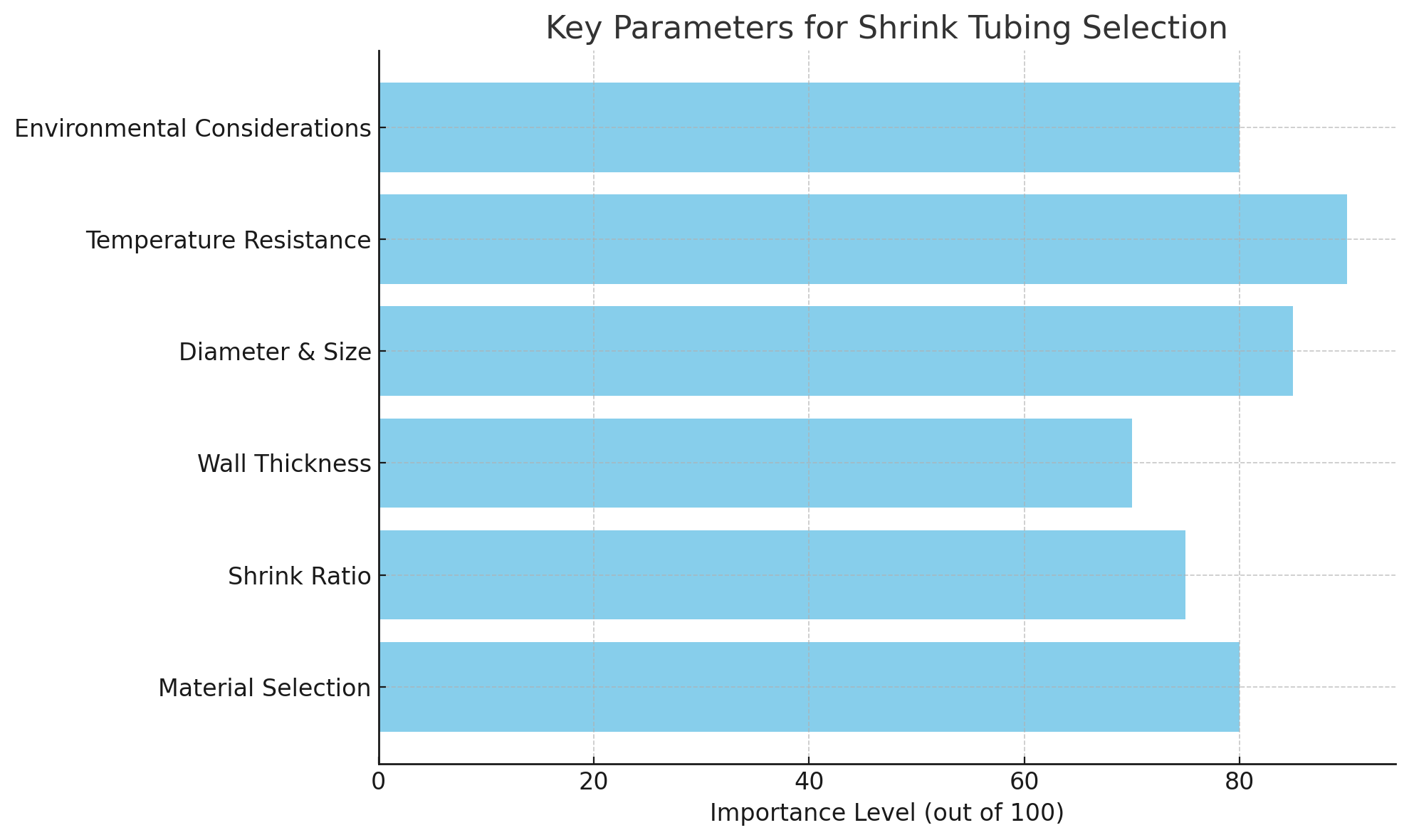
Shrink tubing comes in various shrink ratios, such as 2:1, 3:1, or even 4:1. A 2:1 shrink ratio means the tubing will shrink to half its original size, making it ideal for general applications where there is a moderate difference in sizes between the wire and the tubing. A 3:1 ratio allows for a wider range of component sizes, and a 4:1 ratio offers the most flexibility, ideal for irregular or non-standard shapes.
A 2:1 ratio is common in most wiring applications, but if you're dealing with components of varying sizes or larger cables, a 3:1 or 4:1 ratio might be required for a snug fit.
A higher shrink ratio allows for fewer tubing sizes to cover a wider range of components, offering greater flexibility and reducing the need for multiple tubing sizes.
Shrink Ratio | Shrunk Diameter | Best For | Common Applications |
2:1 | Shrinks to 50% of original size | Standard cables and components | General use, household wiring |
3:1 | Shrinks to 33% of original size | Larger components with varying sizes | Electrical insulation for industrial applications |
4:1 | Shrinks to 25% of original size | Irregularly shaped components or larger variations | Special-shaped or industrial cables |
Single-wall heat shrink tubing is typically used for insulation and light mechanical protection, making it suitable for general indoor applications. Dual-wall tubing, which includes an adhesive lining, offers superior sealing and moisture resistance, making it ideal for outdoor or industrial applications where a waterproof seal is critical.
The thickness of the wall impacts the durability and insulation of the tubing. Heavy-wall tubing offers enhanced mechanical protection against abrasion and is better for environments where cables are exposed to physical stress or harsh chemicals.
Thin-walled tubing is best for applications where flexibility is important, such as for wire harnesses. Medium and heavy-walled tubing should be chosen for applications requiring more robust mechanical protection, such as in industrial machinery or automotive environments.
Properly measuring the diameter of the components to be covered by the tubing is crucial. You should select tubing that is 20-30% larger than the component’s maximum outer diameter to ensure it can slide over the component before shrinking.
The tubing should be long enough to cover the entire exposed area, plus a little extra at the ends. After shrinking, the tubing should provide a tight, secure fit, ensuring that it fully adheres to the surface without gaps.
Selecting tubing that can withstand the temperature range of your application is essential. Polyolefin is suitable for general-use applications with moderate temperature exposure, while PTFE is better for extreme heat, such as in industrial or automotive environments.
Ensure that the selected tubing material matches the operating temperatures of the environment. For instance, high-temperature tubing should be used in engine compartments or other heat-intensive areas.
Dual-wall heat shrink tubing with adhesive lining provides excellent moisture sealing, ideal for outdoor installations or underwater applications. It’s also resistant to corrosion, making it perfect for marine and industrial use.
In chemical processing or oil fields, choosing tubing with strong chemical resistance (such as PTFE or FEP) is critical for ensuring long-term protection and avoiding breakdowns.
For installations exposed to sunlight, UV-resistant heat shrink tubing is essential. UV light can degrade some materials over time, so UV-protective shrink tubing will help extend the life of the cables and connectors.
When selecting tubing for harsh environments, consider factors like abrasion resistance, chemical exposure, and the need for waterproofing. Heavy-duty, dual-wall tubing is ideal for rugged applications like automotive or military systems.
Use a sharp tool to cut the tubing to the correct length, ensuring that it fits properly over the cable or connector with a small overlap.
Before applying heat, make sure the tubing is properly positioned over the cable or connector. This ensures that the tubing will shrink evenly and securely.
Heat guns are a versatile tool for applying heat to tubing in field applications, while heat shrink ovens provide precise and consistent heat for large-scale operations.
When using a heat gun, move it back and forth across the tubing, ensuring that heat is evenly distributed to prevent burning or damaging the tubing.
For tubing with an adhesive liner, ensure the adhesive melts evenly and bonds securely to the surface of the wire or component, providing a strong, waterproof seal.
After heating, inspect the tubing to ensure it has shrunk correctly and there are no gaps or areas where the tubing is not securely bonded.
Make sure to consider the environmental factors that your tubing will be exposed to. Choose materials with the appropriate resistance to heat, chemicals, and moisture.
Not selecting the right material can result in poor performance and premature failure of the tubing, especially in demanding environments.
Manufacturer guidelines provide important details on the proper usage, size, and application of tubing to ensure it performs as expected.
Improper heat application can lead to incomplete shrinkage or damaged tubing, so always follow the recommended temperature instructions.
Mistake | Potential Issue | Solution |
Incorrect Sizing and Fit | Poor protection, gaps, or loose fit | Measure components accurately and select the appropriate size |
Ignoring Environmental Factors | Material breakdown, poor performance | Choose material suited for environmental conditions (e.g., moisture, temperature) |
Not Following Manufacturer Guidelines | Overheating or underheating tubing, poor adhesion | Adhere to manufacturer instructions for temperature and application |
Selecting the right heat shrink tubing is crucial for safe, efficient, and long-lasting electrical installations. Key factors such as material type, shrink ratio, size, and temperature resistance all play a vital role in achieving optimal performance.
For tailored recommendations, consider working with experienced suppliers like Anlian Electric. Their expertise can help guide you in choosing the perfect heat shrink products for your specific needs.
A: Shrink tubing is used for electrical insulation, protecting wires from moisture, chemicals, and physical wear. It is essential for ensuring safe and reliable electrical connections.
A: Heat Shrink Dual Wall Tubings feature an adhesive lining that forms a waterproof seal, making them ideal for outdoor or industrial environments where moisture protection is crucial.
A: Consider material type, shrink ratio, diameter, and environmental conditions like temperature and moisture exposure. Proper sizing ensures a secure fit and optimal protection.
A: Single-wall tubing provides basic insulation and abrasion protection, while dual-wall tubing includes an inner adhesive layer for better sealing, making it suitable for harsher environments.
A: Stress control tubing prevents mechanical damage at cable junctions, ensuring long-lasting insulation and protection against stress, vibrations, and wear.
A: Yes, materials like PTFE heat shrink tubing are designed to withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for applications in automotive, aerospace, and industrial settings.